最近出来的免费的ssl证书,可以用来装个逼。
1.安装mod_ssl,openssl
yum -y install git mod_ssl openssl
2.下载Let’s Encrypt并获取证书
git clone https://github.com/letsencrypt/letsencrypt cd letsencrypt chmod +x letsencrypt-auto ./letsencrypt-auto certonly --standalone --email [email protected] -d xxx.xx -d www.xxx.xx -d xxx.xxx.xx
当看到提示说证书存在/etc/letsencrypt/live/xxx.xx/时,就获取到证书了。
我遇到的问题是防火墙忘了关,导致无法进行服务端校验而无法获取证书。
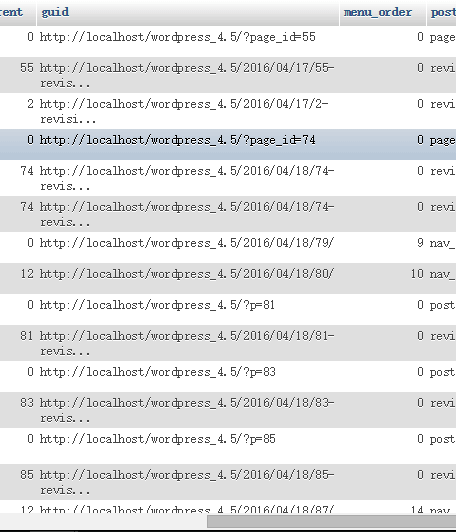
会获取四个证书:

我们进行apache的https升级时需要用到的就下面两个,到时候在配置文件内修改。
3.修改ssl.conf和httpd.conf,仅写出需要修改的部分,并配置强制http跳转https
ssl.conf:
#Listen 443 https DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/xxx" ServerName www.xxx.xx:443 SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/xxx.xx/fullchain.pem SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/xxx.xx/privkey.pem
httpd.conf:
Listen 80 Listen 443 DocumentRoot 自己根目录随意改 跟下面虚拟主机一样就行 <VirtualHost *:80> DocumentRoot xxxx ServerName www.xxx.xx </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:443> DocumentRoot xxxx ServerName www.xxx.xx </VirtualHost>
在web根目录下添加.htaccess,内容为:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{SERVER_PORT} 80
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://www.xxx.xx/$1 [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^www.xxx.xx$ [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://www.xxx.xx/$1 [L,R=301]
4.定时执行
由于其默认90天免费,需要手动续约,所以可以用个定时脚本搞定
更新命令为:
</pre> <pre>./letsencrypt-auto renew</pre> <pre>
保存脚本为renew.sh:
</pre> <pre>#!/bin/sh if ! /绝对路径/letsencrypt/letsencrypt-auto renew > /var/log/letsencrypt/renew.log 2>&1 ; then echo Automated renewal failed: cat /var/log/letsencrypt/renew.log exit 1 fi
通过cron定时运行
添加:
<pre>0 5 * * * root sh /path/to/renew.sh > /dev/null 2>&1